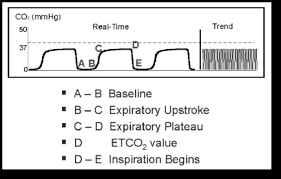
end tidal co2 range cpr
An accurate early predictor of the outcome of resuscitation is needed. Abrupt increase in ETCO2 suggests ROSC during CPR detectable.

End Tidal Carbon Dioxide Etco2 Cerebral Perfusion Pressure Cpp Download Scientific Diagram
MEASURING END-TIDAL CO 2 LEVELS DURING CARDIAC ARREST.

. I can look at those numbers and adjust my ventilator accordingly to keep them within a normal range. Systematic review and meta-analysis of end-tidal carbon dioxide values associated with return of spontaneous circulation during cardiopulmonary resuscitation. Normal ETCO2 in the adult patient.
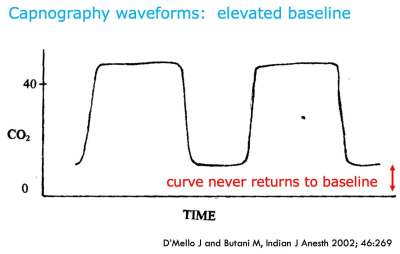
An increase in etCO2 by 5 appears to have reasonable. Although the normal range for CO2 should be between 35-45mmHg CO2 monitoring gives healthcare providers a lot more insight into what is going on with a patients condition. Loss of ETCO2 may be the first sign that CPR is needed.
Remember a normal end-tidal is between 35 and 45. End-tidal carbon dioxide ETco 2 monitoring provides valuable information about CO 2 production and clearance ventilation. Cardio Pulmonary Resuscitation CPR ETCO2 concentration is a reliable index of effective heart compression during CPR which is associated with cardiac output 7 8.
Gradual fall in ETCO2 suggests compressionist fatigue during CPR - time to change compressionists. This will cause a decrease in the ETCO2 end-tidal CO2 and this will be observable on the waveform as well as with the numerical measurement. The purpose of this systematic review is to evaluate the prognostic value of ETCO2 during cardiac arrest and to.
In mmHg the PetCO2 values for those with and without ROSC after five minutes of CPR was. The amount of CO2 at the end of exhalation or end-tidal CO2 ETCO2 is normally 35-45 mm HG. 10 mmHg during CPR in an intubated patient suggests that the quality of chest compressions needs improvement.
The end-tidal carbon dioxide CO2 concentration decreased from a mean - SD of 455 - 088 1 min after chest compression and ventilation was established to values ranging from. 423 20 mmHg versus 34 255 mmHg. Here are five things you should know about waveform capnography in cardiac arrest.
Also called capnometry or capnography this. This causes CO2 to accumulate in the lungs and more of it to be excreted with each breath. End-tidal CO2 may be useful here as an easily and immediately measurable index of changes in cardiac output.

Quantitative Waveform Capnography Acls Medical Training

Average Etco2 Kpa During Cpr In Patients With Or Without Rosc Download Scientific Diagram
Waveform Capnography In The Intubated Patient Emcrit Project

The Impact Of Ventilation Rate On End Tidal Carbon Dioxide Level During Manual Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation Resuscitation

Etco2 Valuable Vital Sign To Assess Perfusion The Airway Jedi

Basic Capnography Interpretation Nuem Blog

The Morphology Of The Normal Capnogram Etco2 End Tidal Carbon Dioxide Icu Nursing Paramedic School Tech School
5 Medical Conditions Where Capnography Can Affect Bls Care Capnoacademy Capnoacademy
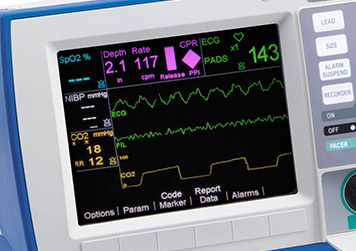
R Series End Tidal Carbon Dioxide Etco2 Zoll Medical

Chest Compressions Induce Errors In End Tidal Carbon Dioxide Measurement Resuscitation
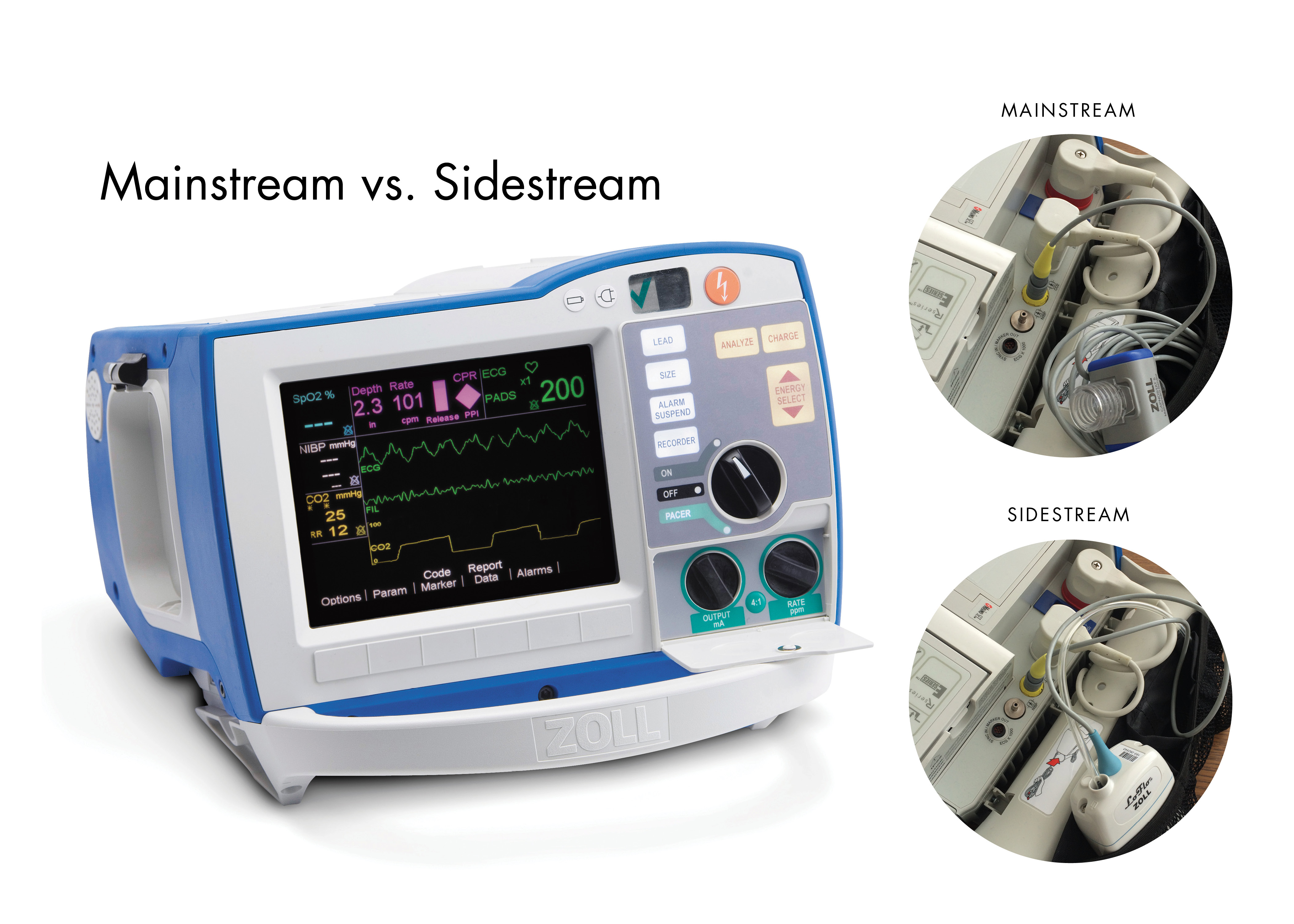
R Series End Tidal Carbon Dioxide Etco2 Zoll Medical

3 Waveform Capnography Showing Changes In The End Tidal Carbon Dioxide Download Scientific Diagram

End Tidal Capnography Can Be Useful For Detecting Diabetic Ketoacidosis Monitoring Copd Page 2 Of 4 Acep Now Page 2

Reversible Causes Of Low Etco2 In Cpr Criticalcarenow

End Tidal Co2 Etco2 By Group And By Group And Rosc A Etco2 Versus Download Scientific Diagram

End Tidal C02 Worth The Investment

End Tidal Carbon Dioxide Etco2 And Ventricular Fibrillation Amplitude Spectral Area Amsa For Shock Outcome Prediction In Out Of Hospital Cardiac Arrest Are They Two Sides Of The Same Coin Resuscitation

What S In A Wave Form Utilizing End Tidal Capnography For More Than Intubation Confirmation Criticalcarenow